What is plasma therapy?
30 November 2025
Plasma therapy has become one of the most discussed modern medical procedures, offering benefits across regenerative medicine, dermatology, orthopedics, autoimmune disorders, and even severe infections. Although it sounds like a futuristic technology, the method is built on one of the body’s oldest and most essential components—blood plasma.
Plasma is the liquid part of blood, making up around 55% of its volume. It contains water, proteins, minerals, antibodies, hormones, and nutrients. Its main role is transportation: carrying nutrients, hormones, immune components, and waste products throughout the body. Because of this rich composition, plasma plays a vital role in immunity, repair, and maintaining healthy balance in the body.
What Is Plasma Therapy?
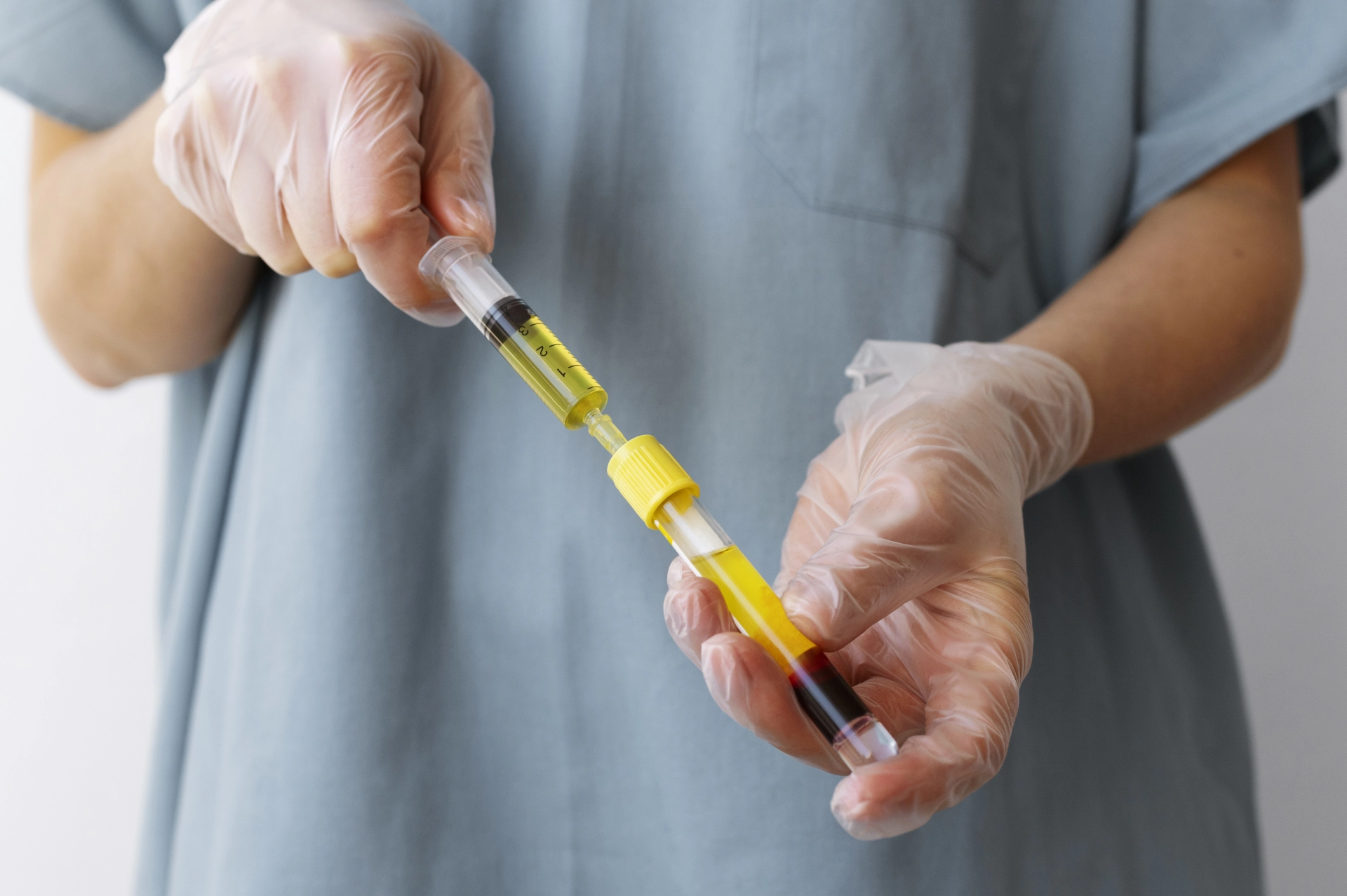
Plasma therapy includes several techniques that use plasma for healing. The most widely used form is Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), where a patient’s blood is processed in a centrifuge to concentrate platelets. These platelets release growth factors that stimulate repair, reduce inflammation, speed wound healing, and improve skin and hair quality. PRP is used in dermatology, cosmetology, orthopedics, sports medicine, and chronic pain treatment.
Another form is convalescent plasma therapy, where plasma from recovered patients transfers antibodies to someone fighting a severe infection. This approach became especially significant during outbreaks such as influenza, SARS, Ebola, and COVID-19. Plasmapheresis is another plasma-based method, used to remove harmful antibodies in autoimmune diseases.
How Plasma Therapy Works
Despite differences between treatment types, their mechanisms are similar. Plasma therapy enhances natural healing by supplying antibodies, stimulating collagen production, activating cell renewal, regulating inflammation, and removing harmful immune substances in autoimmune conditions. These combined effects help tissues recover faster, strengthen the immune response, and improve overall regeneration.
What Conditions Can Plasma Therapy Help With?
The therapy is effective across multiple fields. In infectious diseases, convalescent plasma provides immediate immune support when medications are limited. In autoimmune disorders such as lupus, myasthenia gravis, and Guillain-Barré syndrome, plasmapheresis helps reduce symptoms. PRP is widely used in orthopedics for osteoarthritis, tendon injuries, ligament strains, and muscle tears, helping many athletes avoid surgery. In dermatology and aesthetics, PRP is known for skin rejuvenation, texture improvement, pigmentation reduction, treating acne scars, and supporting hair growth.
Benefits of Plasma Therapy
Because plasma comes from the patient’s own body, it is natural, biocompatible, and carries very low risk of allergic reactions. The procedure is minimally invasive, requires little downtime, and enhances healing in conditions that may not respond well to medication. It can also be safely combined with other treatments.
Risks and Limitations
Although generally safe, plasma therapy may cause mild swelling, temporary discomfort, or dizziness. Rare allergic reactions can occur, and the cost may be higher due to individualized preparation. Results vary from person to person, and donor screening is essential for convalescent plasma use.
How Long Do Results Last?
PRP results typically last between six and twelve months, with improvements building gradually over time. Some patients may require repeated sessions depending on their condition.
Conclusion
Plasma therapy stands at the intersection of natural healing and medical innovation. By using the body’s own plasma, it supports regeneration, strengthens immunity, and opens new possibilities across both medicine and aesthetics. Whether used for serious diseases or cosmetic improvement, plasma therapy continues to transform modern healthcare and enhance quality of life.