Earache is common among children, especially in early childhood. The presence of earache usually means that the child has an ear infection, otitis. Almost all parents deal with ear infections in children. This disease is especially typical for children aged 1-3, but it can also occur at a younger age. According to epidemiological studies, all children up to 5-7 years old get sick with this disease at least once, especially often at the age of 6-12 months. And after that age, from 5-7 years old, ear infections rarely occur. This is due to the structural features of the auditory tube in children.
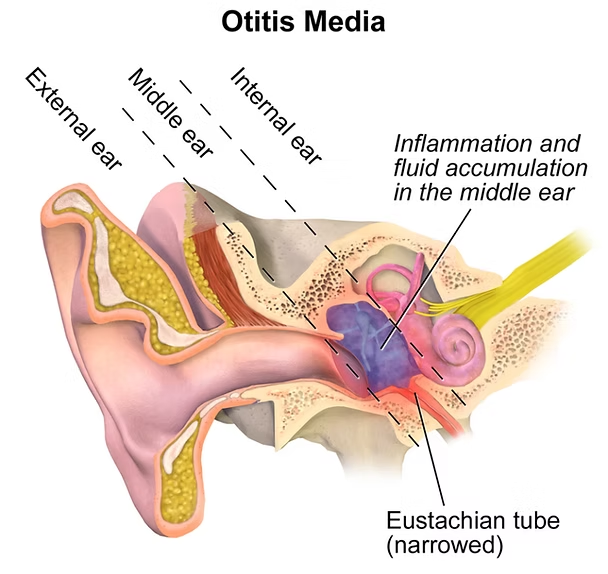
There are external, middle and internal ear infections. External ear infections occur when the infection accumulates around the hairs of the auditory tube, which can also cause an abscess.
Otitis media is a complication of a viral or bacterial infection, or it can occur as a result of a ruptured eardrum. Inflammation of the inner ear occurs as a result of an infection of the paranasal sinuses, inflammation of the meninges, or purulent middle ear inflammation. Otitis media is more common in children.
What are the causes of earache in children?
•
Viral and bacterial infections
, in which the space behind the eardrum becomes inflamed and the middle ear becomes inflamed.
•
Swimmer's ear
, which occurs as a result of irritation of the external auditory canal by water. The main symptom is itching in the auditory canal. If there is an infection, ear pain also occurs.
•
Injury to the auditory canal
, which occurs when a hard object is used to clean the ear. The abrasions can become inflamed, which contributes to the occurrence of pain.
•
An abscess
in the ear canal, which can be very painful.
•
A wax plug
, which is a solid lump of earwax. It causes mild pain, but if the lump goes deeper into the ear canal when you clean the ear with a cotton swab, it can block the ear canal, cause inflammation, pain, and hearing loss in that ear.
•
Foreign bodies
. Children can put various objects in their ears that can cause pain. These are usually small objects found in toys. Do not let your child play with small toys that are not recommended for children of their age, especially without parental supervision.
•
Barotrauma
. During pressure fluctuations, such as on an airplane or in the elevators of high-rise buildings, the eardrum can stretch, which can cause pain, especially when there is a wax plug in the ear.
•
Referred pain
. Earache can be caused by other problems, such as inflammation of the tonsils, jaw, parotid gland, mandibular glands, or teething.
The main signs of ear inflammation are fever, general weakness, restlessness, putting a hand to the ear, crying, ear pain or a feeling of blockage in the ear, decreased hearing, and discharge from the ear.
Sometimes a child may not have earache, but have a high fever and general weakness, nausea, and ear inflammation is confirmed during the examination. This situation is especially common in children under 3 years of age.
The following signs indicate the presence of an external ear infection: fever and ear pain, which increases when chewing and talking.
With inflammation of the middle ear, the child complains of sharp pain in the ear, impaired hearing, and sometimes noise in the ear. There may also be pus production and a fever of up to 38-40 ° С. Breast-fed children may refuse to breastfeed and reach for the sore ear.
Inflammation of the inner ear is characterized by a sharp decrease in hearing, balance disorders, headache, and nausea.
In the absence of treatment, the process can worsen and lead to complications and hearing loss.
Therefore, if you notice such signs in your child, do not self-medicate, immediately contact
our clinic, and our pediatricians will quickly diagnose whether the child has otitis media by examining the ear, and if necessary, refer them to a specialist.
In our clinic, children are treated according to evidence-based principles of medicine: we select only those diagnostic and treatment methods that have proven their effectiveness and never prescribe unnecessary examinations and medications to fully maintain your child’s health.







