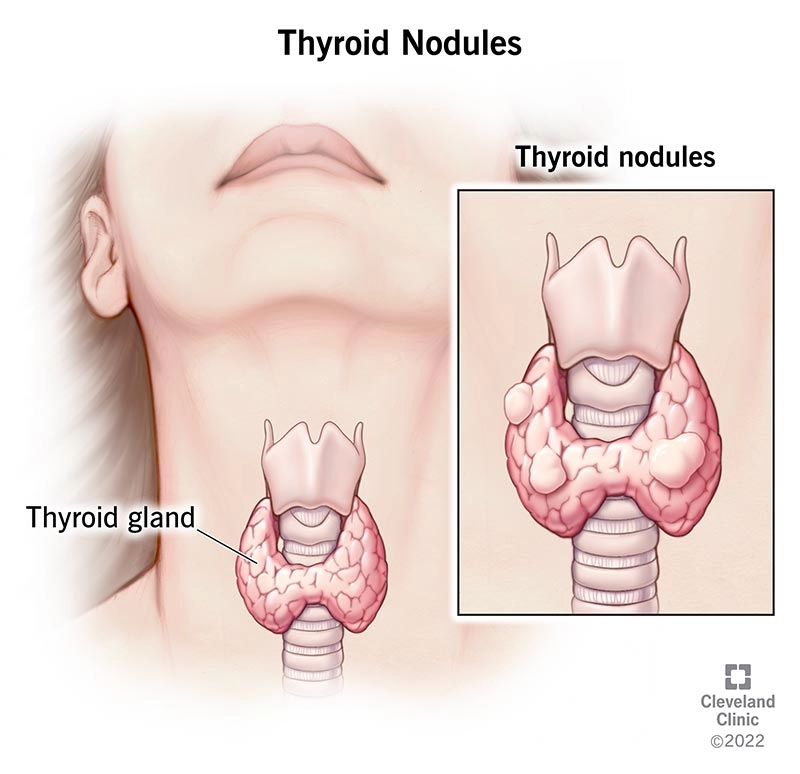
Thyroid nodules are one of the most common medical concerns, especially considering their higher prevalence in women compared to men, even when age is taken into account. This gender difference is largely attributed to the influence of hormones like estrogen and progesterone, which can affect thyroid tissue and contribute to the formation of nodules
The importance of regular monitoring and early detection of thyroid nodules is critical. Early identification can help prevent the progression of various thyroid-related diseases, especially thyroid cancer. It allows for prompt intervention, which can improve outcomes by addressing any issues at the earliest stages.
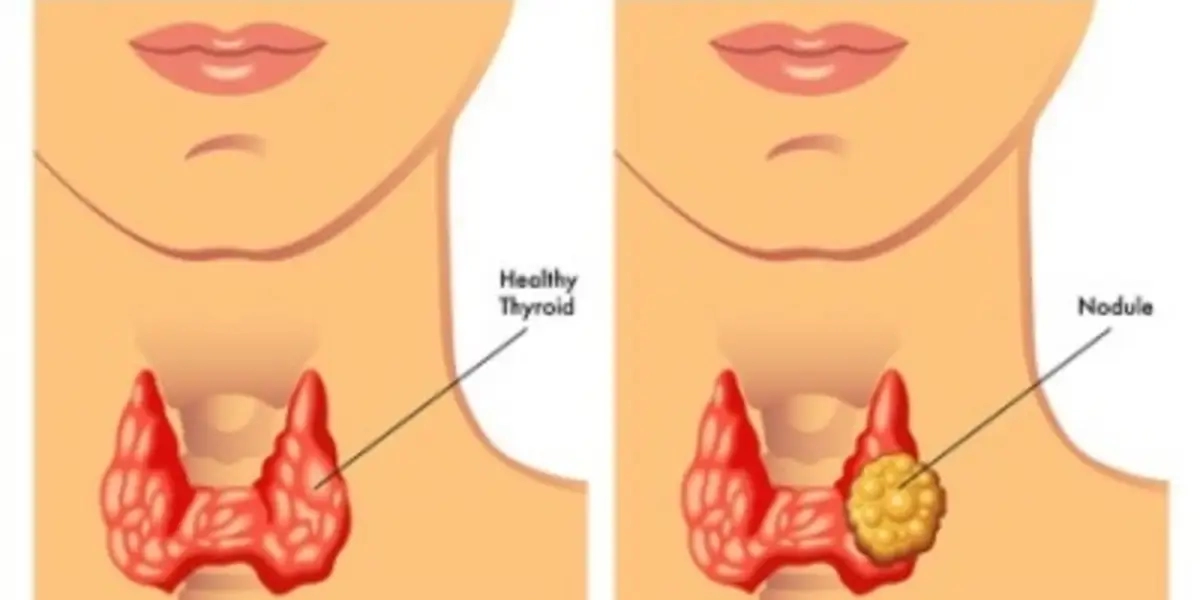
A major concern with thyroid nodules is the possibility of malignancy. While thyroid cancer is relatively rare, it is essential to evaluate nodules carefully to detect any cancerous growths. Without advanced diagnostic tools, identifying malignancy can be challenging, as some cancerous nodules do not show clear signs during a physical examination.
Technological advancements, particularly in imaging, have significantly enhanced the ability to diagnose thyroid nodules accurately. High-resolution ultrasound has become an invaluable tool in detecting these nodules. Research has demonstrated that ultrasound can increase the rate of thyroid nodule detection from around 7% using just palpation to as high as 76% with the use of ultrasound technology. This substantial improvement highlights the crucial role of ultrasound in identifying even small or hard-to-find nodules that might otherwise go undiagnosed.
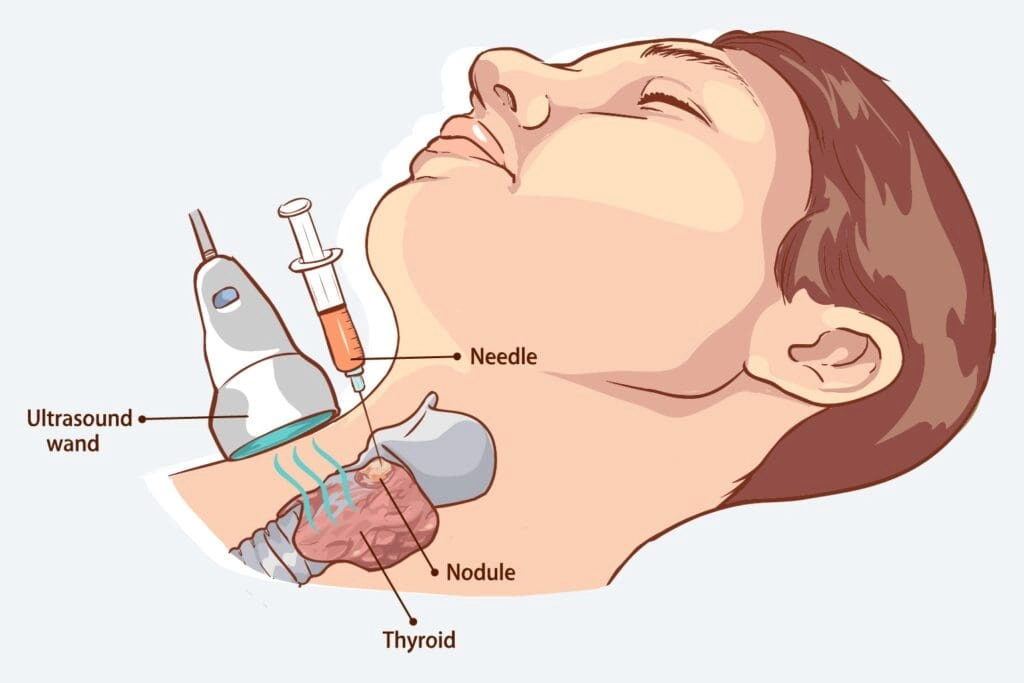
Once a nodule is detected using ultrasound, the next step is determining whether it is benign or malignant. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) has emerged as the most reliable method for evaluating the malignancy of thyroid nodules. This procedure involves using a thin needle to extract a sample of cells from the nodule, which are then analyzed for signs of cancer. When used in conjunction with ultrasound, FNAC provides a minimally invasive but highly accurate diagnostic tool, helping clinicians make informed decisions and reducing unnecessary surgeries
These advancements in diagnostic technology, such as high-resolution ultrasound and FNAC, have revolutionized the approach to thyroid nodules. They significantly improve the accuracy of diagnosis, reduce the risk of missed malignancies, and ensure that patients receive the best possible care.





Fill in the required fields
We will help you quickly find what you need!
