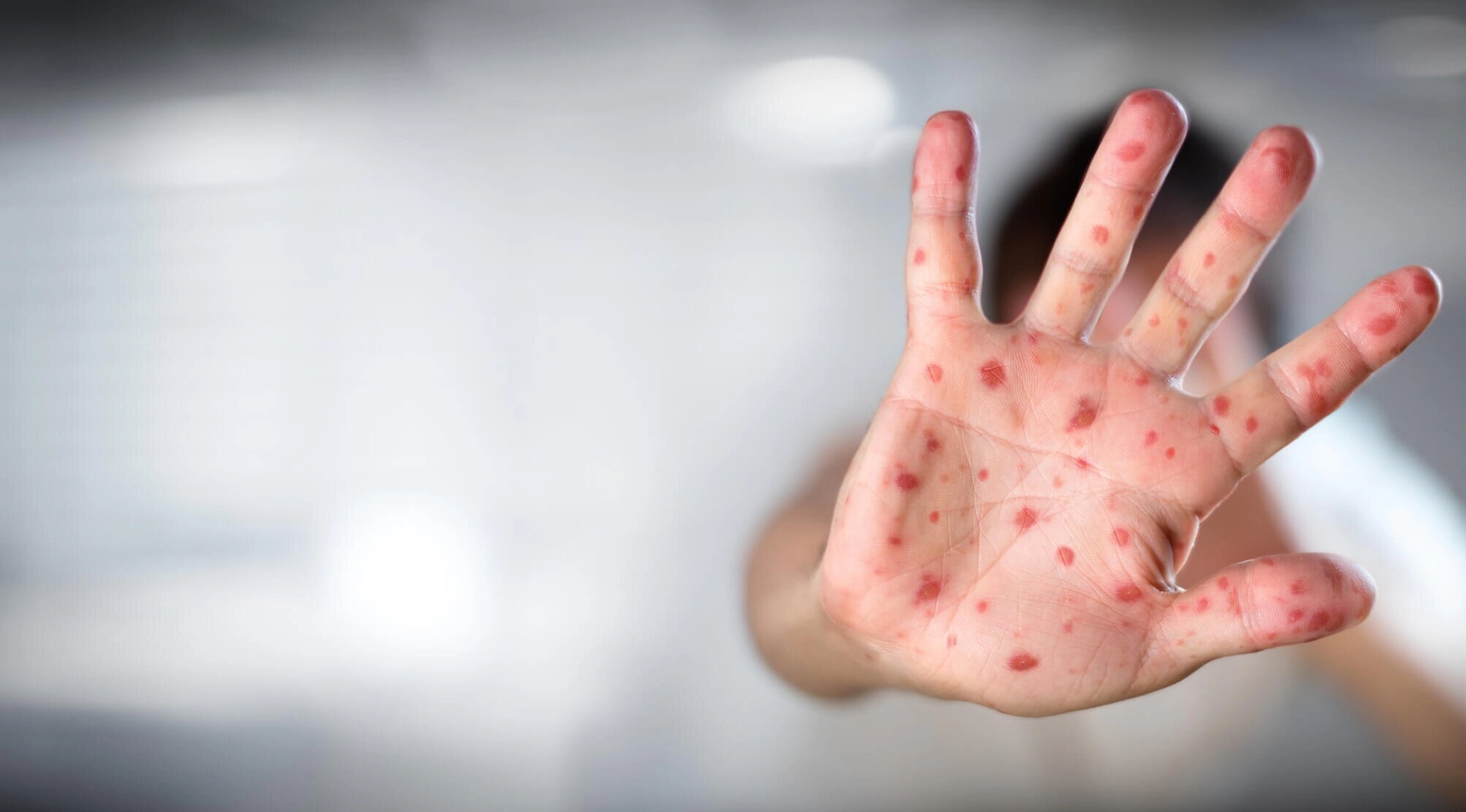
How soon do symptoms appear?
The usual incubation period for rubella is 14 days; with a range of 12 to 23 days.
What are the complications of rubella?
Complications are more common in adult women, who may experience arthritis or joint pain, particularly in the fingers, wrists, and knees. These symptoms usually resolve within a month after the rash appears.
When rubella infects infants during the first trimester of pregnancy, up to 85 percent may develop birth defects and/or neurological issues (known as Congenital Rubella Syndrome, CRS).
What is the treatment for rubella?
There is no specific treatment available for rubella.
When and for how long can someone spread rubella?
Rubella can be transmitted from seven days before the rash appears until seven days after it develops.
Does a previous rubella infection provide immunity?
Yes. Immunity gained from a past rubella infection is typically lifelong.
What is the rubella vaccine?
The rubella vaccine is part of the combined measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. Women of childbearing age should have their immunity tested and receive the rubella vaccine if necessary.