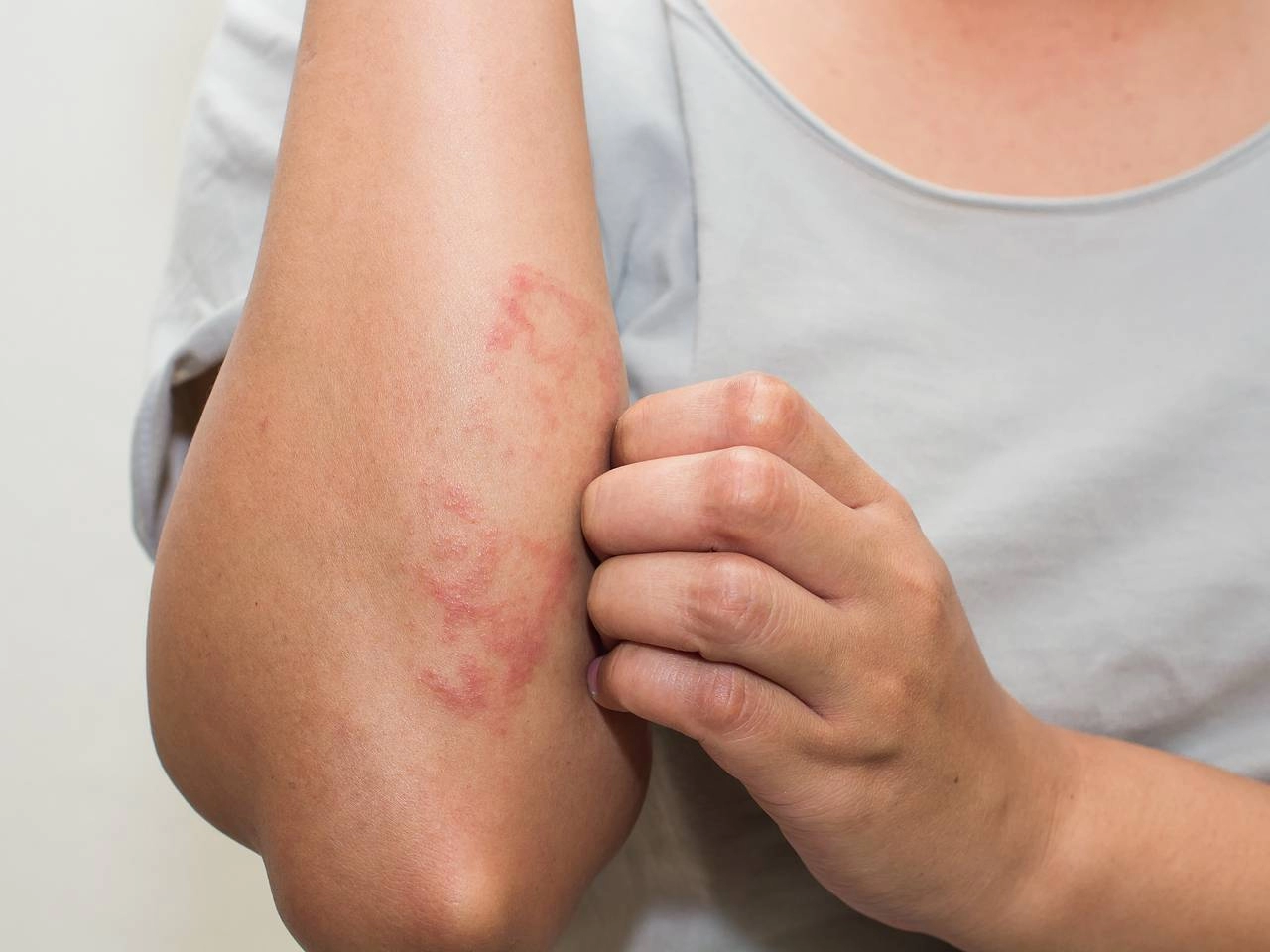
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease that is accompanied by dryness, itching and redness. It occurs in both children and adults and is considered one of the most common skin diseases. The disease progresses in waves, with exacerbations and periods of remission.
In people with atopic dermatitis, the skin does not have a sufficient protective barrier and is more vulnerable to external irritants. In addition to skin symptoms, the disease is often accompanied by other atopic conditions, such as allergic rhinitis or bronchial asthma.
Causes of atopic dermatitis:
1.Hereditary predisposition
If one of the parents has atopic dermatitis, the likelihood of developing the disease in a child increases significantly.
2.Inflammatory immune response
In the case of atopic dermatitis, the immune system reacts excessively to even minor irritants, causing inflammation.
3.Environmental factors
Cold or dry climate, chemical-containing care products, and stress can aggravate or trigger the manifestation of atopic dermatitis.
The main symptoms of atopic dermatitis are:
•Itching, which can be extremely severe, especially at night
•Dryness and flaking of the skin
•Red spots
•Cracks, wounds as a result of scratching
•Skin discoloration, pronounced skin pattern
Approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis
In addition to physical discomfort, the disease also affects a person's quality of life. Itching disrupts sleep, and the appearance of the skin causes social discomfort. Although atopic dermatitis is not completely cured, proper care and treatment can significantly improve the patient's condition and prevent exacerbations.
1.Skin hydration
Moisturizers should be used several times a day, especially after bathing. It is advisable to choose hypoallergenic, fragrance-free creams and balms. Moisturizing care not only reduces dryness, but also helps restore the skin's protective barrier.
Avoid skin care products containing alcohol, sulfates, or preservatives.
2.Drug treatment
Topical corticosteroids are prescribed to treat inflammation. Antihistamines are often used to relieve itching.
How to prevent atopic dermatitis flare-ups:
•Limit bath time to 10 minutes and avoid bathing in very hot water
•Wear cotton clothing, avoiding synthetic or wool clothing
•Keep a food diary to determine possible allergens
•Moisturize the skin 2-3 times a day.
Atopic dermatitis in children:
This condition is often detected in children during the first 6 months of life. Itching and irritation can disrupt sleep and affect a child's behavior. It is important for parents to follow the rules of care and collaborate with a pediatrician or pediatric dermatologist to create the right treatment plan.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic disease, but with the right approach, it is possible to fully control its manifestations. A care regimen, a healthy diet, stress management, and
supervision by a specialist can significantly improve the patient's quality of life.